electron geometry of ch4|ch4 bond angle : Bacolod The electrons that participate in the bond formation and are in the outermost shell of the atom are referred to as valence electrons. Carbon is a p block element present in group 14th and 2nd period in the periodic table and has atomic number of 6. . Tingnan ang higit pa UK’s Top World of Tanks Betting Sites; World of Tanks Gambling Sites Bonus Offers Highlights Rating: Secure Link: T&C’s; 🥇 BetVictor: Bet £10 Get £30 In Free Bets: 6, 93.75%, Live Streaming: 5/5 Score: Visit Site! Full T&Cs Apply! 18+ New customers only. Opt in, bet £10 (odds 2.00+) on any football market within 7 days of registration.
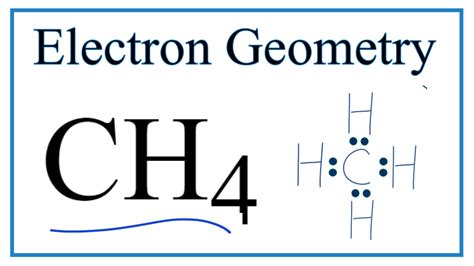
electron geometry of ch4,There are four bonding pairs of electrons, so to keep their repulsive forces at a minimum, they take the tetrahedral molecular geometry. Hence, CH 4 or Methane has a Tetrahedral Molecular geometry. CH4 Bond Angles. One can use AXN Notation to find out the molecular geometry and the . Tingnan ang higit paThe electrons that participate in the bond formation and are in the outermost shell of the atom are referred to as valence electrons. Carbon is a p block element present in group 14th and 2nd period in the periodic table and has atomic number of 6. . Tingnan ang higit paFor the CH4molecule, we will find the Carbon atom’s hybridization as it is the one sharing electrons with Hydrogen atoms and forming bonds. So for finding out the hybridization for the Carbon atom, we will find out the Steric Number. Steric Number- . Tingnan ang higit pa
Lewis structure is the pictorial representation of the arrangement of valence shell electrons in the molecule, which helps us understand the atoms’ bond . Tingnan ang higit pach4 bond angleMolecular geometry helps us understand the arrangement of atoms in 3D for any given molecule. For the Methane molecule, . Tingnan ang higit pa

Learn how to draw the lewis structure of methane (CH4) and understand its geometrical and hybridization properties. The web page explains the valence electrons, octet rule, VSEPR theory, and . Learn how to draw the lewis structure of methane (CH4) and understand its geometrical and hybridization properties. The web page explains the valence electrons, octet rule, VSEPR theory, and .
In this video we look at the electron geometry for Methane (CH4). Because the methane molecule has four electron domains (four hydrogen atoms and no lone .electron geometry of ch4 ch4 bond angle An explanation of the molecular geometry (and Electron Geometry) for the CH4 (Methane) including a description of the CH4 bond angles.

Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion. Methane has 4 regions of electron density around the central carbon atom (4 bonds, no lone pairs). The resulting shape is a regular tetrahedron with H-C-H angles of 109.5°.
We can use the VSEPR model to predict the geometry of most polyatomic molecules and ions by focusing only on the number of electron pairs around the central atom, ignoring . What is the proposed molecular geometry for CH4? Let’s begin by drawing a Lewis structure for methane. To determine the molecular geometry or shape of this .
Learn how to draw the CH4 Lewis structure and understand its tetrahedral shape and nonpolar nature. Find out the valence electrons, formal charge, and FAQs of this .Determine the Electron geometry from the Lewis dot structure. Determine the molecular geometry. It is very important from the onset that students understand the difference between electronic geometry . Identify the electron-pair geometry based on the number of regions of electron clouds: linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, or octahedral (Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\), first column).Figure 8.6.1 8.6. 1 shows the various molecular geometries for the five VESPR electronic geometries with 2 to 6 electron domains. When there are no lone pairs the molecular geometry is the electron (VESPR) .CH 4 contains 4 bonded and no nonbonded electron domains, giving tetrahedral e-domain and molecular geometries. (AX 3 E 1).The H-C-H bond angles (109.5 degrees) are those predicted for a perfect tetrahedral geometry. Use your mouse (computer) or fingers (touch screen) to manipulate the Jmol model.
2. The carbon atom forms two double bonds. Each double bond is a group, so there are two electron groups around the central atom. Like BeH 2, the arrangement that minimizes repulsions places the groups 180° apart. 3. Once again, both groups around the central atom are bonding pairs (BP), so CO 2 is designated as AX 2.Trigonal Bipyramidal Electron Geometry. A central atom with five pairs of bonding electron pairs is known as trigonal bipyramidal. It has the shape of three pairs in a plane at 120° angles (the trigonal planar geometry) and the remaining two pairs at 90° angles to the plane. The shape is similar to two pyramids joined by a triangular base. As stated above, molecular geometry and electron-group geometry are the same when there are no lone pairs. The VSEPR notation for these molecules are AX n. "A" represents the central atom and n represents the number of bonds with the central atom. When lone pairs are present, the letter E x is added. The x represents the number .electron geometry of ch4VSEPR calculation for methane, C H 4. The calculation for methane shows that the carbon atom is associated with 8 electrons in the σ framework. This corresponds to four shape-determining electron pairs. The coordination geometry of carbon is consequently tetrahedral. There are four bonded groups, therefore there are no lone pairs. The .The molecular geometry of CH4 is tetrahedral. This means that the four hydrogen atoms are arranged around the central carbon atom in a way that forms a pyramid-like shape. . The valence electron count determines the number of electrons an atom can share with other atoms to form covalent bonds. In the case of CH4, the carbon atom has four .Ammonia, NH3, is a pyramid-shaped molecule, with the hydrogens in an equilateral triangle, the nitrogen above the plane of this triangle, and a H-N-H angle equal to 107°. The geometry of CH4 is that of a tetrahedron, with all H-C-H angles equal to 109.5°. (See also Figure.) Ethane, C2H6, has a geometry related to that of methane.
electron geometry of ch4|ch4 bond angle
PH0 · po4 3 electronic geometry
PH1 · electron geometry vs molecular geometry
PH2 · electron geometry chart
PH3 · electron and molecular geometry table
PH4 · ch4 lewis structure
PH5 · ch4 hybridization
PH6 · ch4 bond angle
PH7 · Iba pa